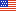
| 1766 |
First edition of The Nautical Almanac and Astronomical Ephemeris,
published by Astronomer Royal of England, with data for 1767. |
| 1852 |
First edition of The American Ephemeris and Nautical Almanac, with
data for 1855. The US book publishes part of its data using the prime
meridian of Washington, and part using the prime meridian of Greenwich. |
| 1900 |
First edition based on Newcomb and Hill's planetary ephemerides and other research being performed in the office since 1877. |
| 1912 |
U.S. Congress authorizes the international exchange of data. The
official collaboration between the US and UK begins and continues
today. |
| 1916 |
International cooperation commenced with this volume. |
| 1925 |
Civil time introduced with notation GCT. Day change to begin at midnight instead of noon. |
| 1941 |
Almanacs adopt FK3 as the fundamental reference system |
| 1953 |
Use of term GCT eliminated from this issue. It was first introduced in the 1925 edition. |
| 1955 |
Agreed with the British Nautical Almanac Office that, beginning with the volume for 1960, the contents of the American Ephemeris and the British Nautical Almanac will be identical. Half of the production will be done in the U.S. and half in England, and the printing will be done independently in the two countries. The unified volume is used in Germany in place of the former Berliner Jahrbuch (which has been discontinued); and parts of the volume are reproduced in the Japanese Ephemeris. |
| 1960 |
The title The Astronomical Ephemeris replaces, without loss of
continuity of content, the previous UK title The Nautical Almanac and
Astronomical Ephemeris. The Astronomical Ephemeris and the
American Ephemeris and Nautical Almanac become identical in content.
The US and UK each produce about 50% of the work. |
| 1961 |
First edition of the Explanatory Supplement to the Astronomical Almanac is published. Explains the derivation and contents of the annual book. |
| 1964 |
Almanacs adopt FK4 as the fundamental reference system. |
| 1968 |
In accordance with the recommendations of the 12th General Assembly of the International Astronomical Union (IAU), the IAU 1964 constants were adopted beginning with this volume. |
| 1968 |
With the edition for 1968, there was included a "Supplement to the A.E. 1968" containing the exposition of the IAU System of Astronomical Constants. Reprints of this Supplement were printed. |
| 1972 |
With the edition for 1972, additional precision was given for: tabulated longitude of the Sun, half day values of the horizontal parallax of the Moon, and tabulated true distance of the planets from Earth. Minor planets ephemerides were given throughout the year. A new section, the Moon's distance in units of Earth's equatorial radius, was added. |
| 1974 |
With the edition for 1974, preliminary pages were re-organized and notes on the visibility of the planets were added. The physical ephemerides of Mars and Saturn were extended to cover the entire year. |
| 1981 |
The 1981 edition was reformatted, the named changed to The Astronomical Almanac and a single printing performed in the US for shipment to England. The division of labor was completely redefined. |
| 1981 |
Stars and Stellar Systems Section added. |
| 1982 |
With the edition for 1982, data for sigma Octantis was introduced in addition to Polaris. A method of providing precise latitude and azimuth in the Southern Hemisphere, and a formula for Pole star was added. A table of geocentric rectangular coordinates of the Sun was included. |
| 1984 |
With the edition for 1984, the International Astronomical Union 1976 constants and FK5 (J2000) system was adopted. Ephemeris Time (ET) was replaced with Barycentric Dynamic Time (TDB) and Terrestrial Dynamical Time (TDT). The basis for the ephemerides was changed to Jet Propulsion Laboratory's DE200/LE200. |
| 1984 |
The edition for 1984 included a Supplement to the Astronomical Almanac 1984, which detailed the introduction of the improved IAU System of Astronomical Constants, Time Scales and Reference Frame into The Astronomical Almanac. |
| 1992 |
Second edition of the Explanatory Supplement to the Astronomical Almanac is published. |
| 2003 |
DE405/LE405 Jet Propulsion Laboratory planetary ephemerides adopted.
Major revision of minor planet section. The Hipparcos Catalogue is the basis for the stellar data, replacing the FK5. |
| 2006 |
IAU/IERS "interim" precession and nutation models incorporated. |
| 2009 |
Finalized IAU precession and nutation models incorporated. |
| 2011 |
The edition for the 2011 included a list of exoplanets and host stars. Lunar librations are derived from JPL's LE403 lunar rotation ephemeris. |
| 2012 |
The edition for the 2012 introduced Minor Planet Center (MPC) codes in the Observatory List. |
| 2013 |
Third edition of the Explanatory Supplement to the Astronomical Almanac is published. |
| 2013 |
Pluto data reorganized and added to newly named Section G, Dwarf Planets & Small Solar System Bodies. |
| 2015 |
Jet Propulsion Laboratory's DE430/LE430 planetary ephemerides was adopted. The IAU 2012 resolution on the re-definition of the astronomical unit of length was implemented. Predicting magnitude and surface brightness of planets was updated to account for the geometry of oblate planets. |
| 2016 |
The basis for Ceres ephemeris is now Jet Propulsion Laboratory's Horizons data. |
| 2019 |
The physical data for many solar system bodies was updated to values in the Report of the IAU Working Group on Cartographic Coordinates and Rotational Elements: 2015 [Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astr. (2018), 130:22.] |